Product Name :
CD235a Recombinant Protein Swiss-Prot :
P02724 Host :
E.coli Tag :
Amino acid Sequence :
MSSTTGVAMHTSTSSSVTKSYISSQTNDTHKRDTYAATPRAHEVSEISVRTVYPPEEETGERVQLAHHFSEPE Restriction sites :
NdeI-XhoI Background :
The chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assay is a powerful and versatile technique used for probing protein-DNA interactions within the natural chromatin context of the cell. This assay can be used to either identify multiple proteins associated with a specific region of the genome or to identify the many regions of the genome bound by a particular protein. ChIP can be used to determine the specific order of recruitment of various proteins to a gene promoter or to "measure" the relative amount of a particular histone modification across an entire gene locus. In addition to histone proteins, the ChIP assay can be used to analyze binding of transcription factors and co-factors, DNA replication factors, and DNA repair proteins. When performing the ChIP assay, cells are first fixed with formaldehyde, a reversible protein-DNA cross-linking agent that "preserves" the protein-DNA interactions occurring in the cell. Cells are lysed and chromatin is harvested and fragmented using either sonication or enzymatic digestion. Fragmented chromatin is then immunoprecipitated with antibodies specific to a particular protein or histone modification. Any DNA sequences that are associated with the protein or histone modification of interest will co-precipitate as part of the cross-linked chromatin complex and the relative amount of that DNA sequence will be enriched by the immunoselection process. After immunoprecipitation, the protein-DNA cross-links are reversed and the DNA is purified. Standard PCR or quantitative real-time PCR are often used to measure the amount of enrichment of a particular DNA sequence by a protein-specific immunoprecipitation. Alternatively, the ChIP assay can be combined with genomic tiling micro-array (ChIP on chip) techniques, high throughput sequencing (ChIP-Seq), or cloning strategies, all of which allow for genome-wide analysis of protein-DNA interactions and histone modifications. SimpleChIP® primers have been optimized for amplification of ChIP-isolated DNA using real-time quantitative PCR and provide important positive and negative controls that can be used to confirm a successful ChIP experiment. Soluble :
PBS, 4M Urea, PH7.4 Purification&Purity :
Transferred into competent cells and the supernatant was purified by NI column affinity chromatography and the purity is > 85% (by SDS-PAGE). Storage&Stability :
Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze-thaw cycles. Expression vector :
pet-22b(+) BiowMW :
~11kDa Note :
For research use only, not for use in diagnostic procedure. concentration :
CD235a Recombinant Protein Swiss-Prot :
P02724 Host :
E.coli Tag :
Amino acid Sequence :
MSSTTGVAMHTSTSSSVTKSYISSQTNDTHKRDTYAATPRAHEVSEISVRTVYPPEEETGERVQLAHHFSEPE Restriction sites :
NdeI-XhoI Background :
The chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assay is a powerful and versatile technique used for probing protein-DNA interactions within the natural chromatin context of the cell. This assay can be used to either identify multiple proteins associated with a specific region of the genome or to identify the many regions of the genome bound by a particular protein. ChIP can be used to determine the specific order of recruitment of various proteins to a gene promoter or to "measure" the relative amount of a particular histone modification across an entire gene locus. In addition to histone proteins, the ChIP assay can be used to analyze binding of transcription factors and co-factors, DNA replication factors, and DNA repair proteins. When performing the ChIP assay, cells are first fixed with formaldehyde, a reversible protein-DNA cross-linking agent that "preserves" the protein-DNA interactions occurring in the cell. Cells are lysed and chromatin is harvested and fragmented using either sonication or enzymatic digestion. Fragmented chromatin is then immunoprecipitated with antibodies specific to a particular protein or histone modification. Any DNA sequences that are associated with the protein or histone modification of interest will co-precipitate as part of the cross-linked chromatin complex and the relative amount of that DNA sequence will be enriched by the immunoselection process. After immunoprecipitation, the protein-DNA cross-links are reversed and the DNA is purified. Standard PCR or quantitative real-time PCR are often used to measure the amount of enrichment of a particular DNA sequence by a protein-specific immunoprecipitation. Alternatively, the ChIP assay can be combined with genomic tiling micro-array (ChIP on chip) techniques, high throughput sequencing (ChIP-Seq), or cloning strategies, all of which allow for genome-wide analysis of protein-DNA interactions and histone modifications. SimpleChIP® primers have been optimized for amplification of ChIP-isolated DNA using real-time quantitative PCR and provide important positive and negative controls that can be used to confirm a successful ChIP experiment. Soluble :
PBS, 4M Urea, PH7.4 Purification&Purity :
Transferred into competent cells and the supernatant was purified by NI column affinity chromatography and the purity is > 85% (by SDS-PAGE). Storage&Stability :
Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze-thaw cycles. Expression vector :
pet-22b(+) BiowMW :
~11kDa Note :
For research use only, not for use in diagnostic procedure. concentration :
Blocking peptide available as NCP0368P

 CD235a Recombinant Protein
CD235a Recombinant Protein 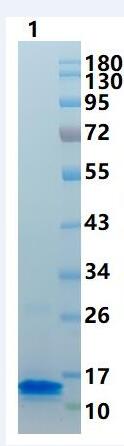
 Datasheet
Datasheet COA
COA MSDS
MSDS SHIP
SHIP